Gene Screening
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) is an IVF technology that assesses the genetic makeup of embryos before transfer and is an important part of preventive medicine. By conducting molecular genetic screening and diagnosis of genetic diseases at the embryonic stage, it selects embryos without disease phenotypes for uterine transfer. Compared with prenatal diagnosis, the advantage of PGT is that it screens and diagnoses embryos before implantation, achieving better births from the very beginning of pregnancy. This is especially true for women who have experienced recurrent miscarriages and those of advanced maternal age. PGT can effectively increase their chances of successful pregnancy by screening for aneuploidy and structural abnormalities in embryos.
PGT-A, PGT-M, and PGT-SR Technologies: Protecting Your Baby
PGT is a suite of highly precise genetic diagnostic techniques used to detect whether embryos carry specific genetic diseases or have certain chromosomal abnormalities.
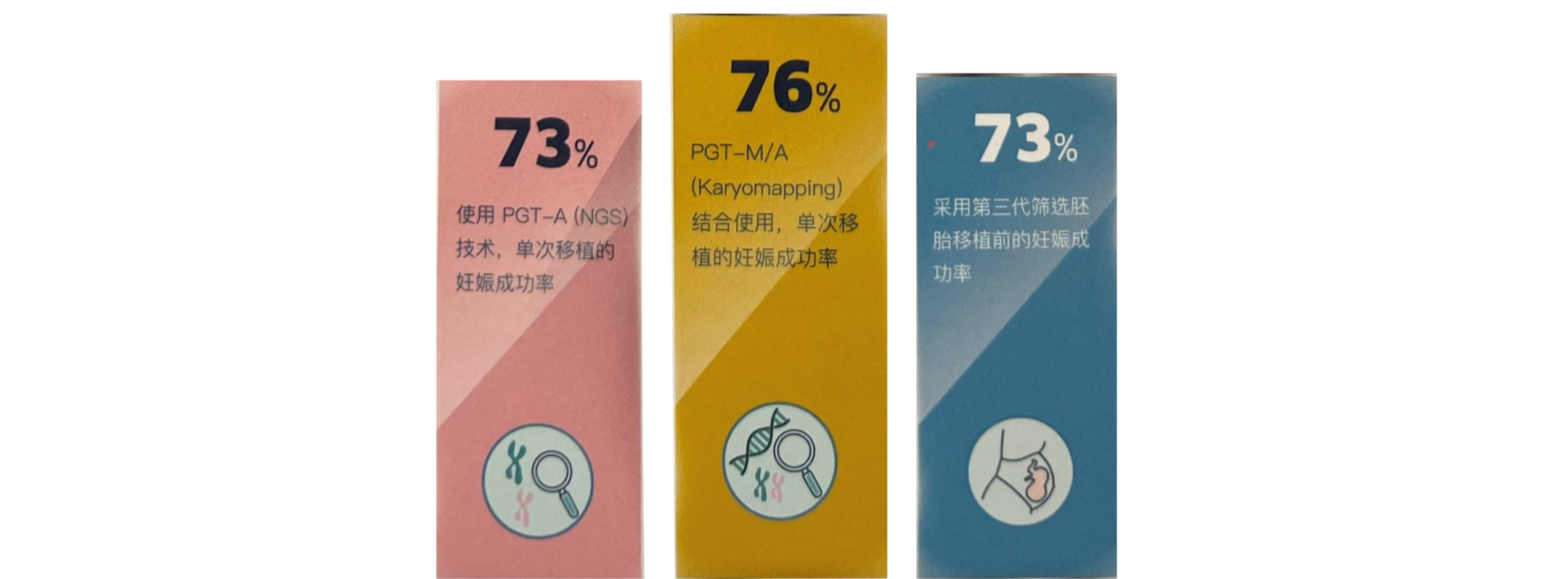
PGT-A
PGT-A (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy) is suitable for older couples, those with a history of recurrent miscarriages, or patients who have experienced failed embryo transfers. Its purpose is to screen embryos for the correct number of chromosomes, thereby reducing the risk of miscarriage and increasing the live birth rate.
PGT-SR
PGT-SR (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Structural Rearrangements) is suitable for couples where one or both partners carry balanced chromosomal structural rearrangements, such as translocations or inversions. The purpose of PGT-SR screening is to select balanced embryos to maximize the chances of a healthy pregnancy.
PGT-M
PGT-M (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic/Single Gene Defects) is suitable for couples who do not have fertility issues but carry a serious genetic disease, such as thalassemia, spinal muscular atrophy, hemophilia, etc. PGT-M is used to select embryos that do not have the serious genetic disease, and these patients will also undergo PGT-A.
The Scientific Technology Used in PGT
NGS (Next-Generation Sequencing) is a preimplantation genetic testing technology that examines all 23 pairs of chromosomes in developing embryos, including chromosomes 1-22 and the XY chromosomes. It enables scientists to select only embryos with the correct number of chromosomes for transfer. NGS is used in PGT-A and PGT-SR
Karyomapping is a highly precise and complex preimplantation genetic testing technique that can be used to detect whether an embryo carries a known serious single-gene disorder. Karyomapping is used in PGT-M and can also provide PGT-A screening at the same time.
Advantages of Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy (PGT-A) can:
- Increase the likelihood of embryo implantation
- Enhance the rate of ongoing pregnancy
- Boost confidence in single embryo transfer (SET)
- Reduce the risk of miscarriage
- Improve the live birth rate
- Decrease the time required for patients to achieve pregnancy
- Lower the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in children
- Discovering fetal chromosomal abnormalities during pregnancy puts parents in a difficult position: to terminate the pregnancy or to give birth to the child?
PGT can reduce the risk of parents having to make such a difficult choice.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic/Single Gene Defects (PGT-M) can:
- Prevent your baby from having known familial genetic diseases
- Perform human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing so that after the baby is born, it can provide umbilical cord blood stem cells to cure another child who is already ill.